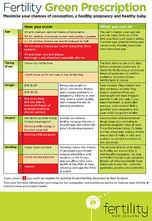
Public funding of fertility treatment
Funding
Requirements for publicly funded treatment differ slightly by District Health Board, but these criteria include:
- The couple have been trying to conceive for at least twelve months (for single people and same-sex couples, refer to ‘Making Babies with Donors and Surrogates’)
- If there is no diagnosed reason for infertility (‘unexplained infertility’), the couple must have been trying to conceive for five years
- Woman’s age 39 or less at time of consultation
- Woman’s BMI 32 or less
- Woman must be a non-smoker (at least three months prior to application)
- NZ citizenship, residency or visa of at least two years’ in duration (for both partners)
Auckland and Northland
If the couple have 2 or more children at home under the age of 12 they are not eligible for publicly funded fertility treatment.
Women with a BMI >32 and / or smoke may be eligible for a First Specialist Appointment (FSA) but they will not be eligible for publicly funded treatment.
Criteria for publicly funded treatment:
- In addition to the criteria for eligibility for FSA, residency status must apply for the duration of the treatment (that is, have a minimum of 20 months guaranteed residency at the time of FSA) and during the treatment the couple must provide a New Zealand contact address.
- A woman can be eligible for treatment when she is >=40 years of age as long as the referral was sent when she was <40 years of age.
- A man can be eligible for treatment when he is >=55 years of age as long as the referral was sent when he was <55 years of age.
- A woman must have a BMI <= 32 to be eligible for publicly funded treatment. This is a healthy weight which increases her chance of having a successful pregnancy and healthy baby. She must also be clinically fit for fertility treatment and pregnancy.
- A man must have a BMI < 40 to be eligible for publicly funded treatment.
- If FSH is >15, a couple may have one cycle using the woman’s own egg. If this is not successful, they are only eligible for further treatment using a donor egg.
- A couple have to both be non-smokers for three months to be eligible for treatment. Non-smoker means no smoking at all in the last three months.
- A couple are not eligible for publicly funded treatment if there is documented evidence of illicit drug use or alcohol abuse in the last 12 months.
- Couples with unexplained infertility alone (with no other contributing factors to their infertility) need to have a duration of infertility of 5 years before they will be eligible for treatment.
- If the time between FSA and being eligible for treatment is more than 3 months (for example in the case of unexplained infertility < 5 years), the couple will be discharged following FSA and will need to see their GP and request another referral to Fertility services at a later stage or if their circumstances change.
- Patients waiting for IVF should have a postal address and a contact phone number in New Zealand. Patients have a responsibility to update their address and contact details with the clinic that they are enrolled with.
- Patients must be living in New Zealand when their treatment commences and remain living in New Zealand throughout the duration of their treatment.
- If letters from a clinic to a patient are returned after two attempts, at least one month apart and two phone calls are not answered, the clinic can send a letter to the patient informing them that they are no longer on the waiting list for fertility treatment, with a copy to the referrer (e.g. GP).
- The clinic must inform the patient of their responsibilities with regard to providing up to date contact details and the consequences of failing to do so at the time of enrolment.
- If patients move regions within New Zealand they must notify the clinic they are enrolled with to request transfer to a local fertility clinic.
Waikato/Tauranga/Rotorua/Taranaki
If a couple, both must have NZ residency, citizenship or a work visa showing at least 2 years. If single, must have NZ residency, citizenship or a work visa showing at least 2 years.
- Women must be 39 years of age or younger at the time of referral
- A women’s BMI must be no greater than 32.
- Couples cannot have two or more children under the age of 12 living at home
- Both partners must be eligible to receive health services in NZ.
- If you are 35 years or younger, you also need to have been trying to get pregnant for at least 18 months or for women over 35 years you must have been trying for 12 months,
- - Or have a severe male or female factor, such as no or very poor-quality sperm or failure to ovulate,
- - Or have a genetic condition that can be treated with pre-implantation genetic diagnosis,
- - Or have an indication for fertility preservation.
Rest of North Island
If a couple, both must have NZ residency, citizenship or a work visa showing at least 2 years. If single, must have NZ residency, citizenship or a work visa showing at least 2 years.
- Women must be 39 years of age or younger at the time of referral
- A women’s BMI must be no greater than 32.
- Couples cannot have two or more children under the age of 12 living at home
- If you are 35 years or younger, you also need to have been trying to get pregnant for at least 18 months or for women over 35 years you must have been trying for 12 months,
- - Or have a severe male or female factor, such as no or very poor-quality sperm or failure to ovulate,
- - Or have a genetic condition that can be treated with pre-implantation genetic diagnosis,
- - Or have an indication for fertility preservation.
South Island
If a couple, both must have NZ residency, citizenship or a work visa showing at least 2 years. If single, must have NZ residency, citizenship or a work visa showing at least 2 years.
- Women must be 39 years of age or younger at the time of referral
- Couples cannot have two or more children under the age of 12 living at home.
- A women’s BMI must be no greater than 32.
- Couples must have been trying to get pregnant for at least 12 months:
- - Or have a severe male or female factor, such as no or very poor-quality sperm or failure to ovulate.
- - Or have a genetic condition that can be treated with pre-implantation genetic diagnosis,
- - Or have an indication for fertility preservation.